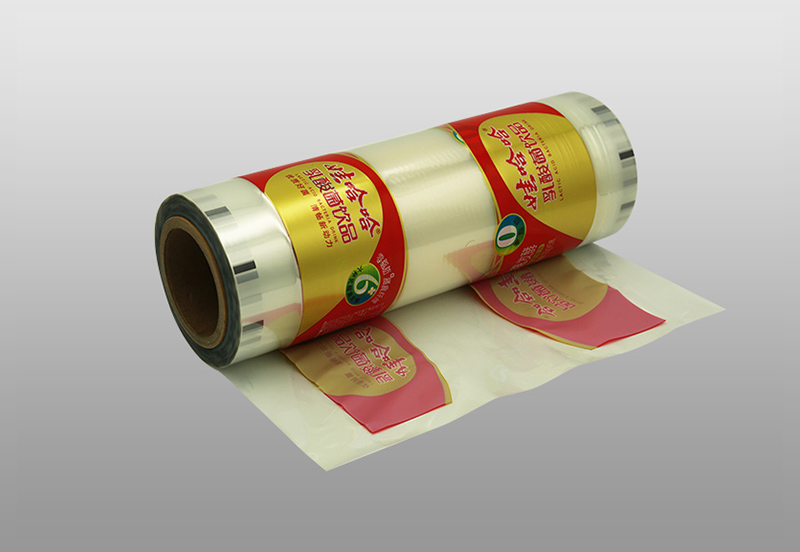
Unlike paper labels, heat shrinkable films use non-absorbent printing materials such as PVC, PP, PETG, OPS, OPP, and various multi-layer co-extruded films. The nature of such materials determines its printing process and paper labels different. In traditional offset printing, embossing (flexo printing), gravure printing and silk screen printing, the printing method of heat shrinkable film labels is still mainly gravure printing. The main reason is that the domestic gravure printing presses are large and the printing cost is fiercely competitive. , And gravure printing has the characteristics of thick ink layer, bright colors and rich layers, and this type of label is mostly long-run, and the printing force of the gravure plate can reach several million sheets, so for large-volume printing In terms of jobs, it is undoubtedly the most cost-effective. However, with the increasingly fierce market competition, coupled with the development of flexographic plate making, machinery, ink and other technologies, the proportion of flexographic printing has increased year by year.
1. Tension control
Since the film is more susceptible to changes in tension during the printing process, resulting in inaccurate overprinting, it is necessary to pay great attention to tension control during the printing process to maintain a stable and balanced tension. The size of the tension adjustment should be determined according to the type and tensile strength of the film. For example, the tensile strength of the film is weak, and it is easy to stretch and deform, and the tension should be smaller; for the film with stronger tensile strength, The tension can be correspondingly greater. In the case of a certain type of film, the width and thickness of the film are also important factors that determine the magnitude of the tension. A wide film should have a greater tension than a narrow film, and a thicker film has a greater tension than a thin film.
Gravure heat shrinkable film mainly uses a unit type gravure printing machine. Now such machines are equipped with an automatic tension control system and an automatic color registration control system. The uncoiling area, printing area and winding area are automatically adjusted according to the measured error between the color registration marks. Zone tension to ensure the stability of the tension during the printing process and the accuracy of the final overprint. Compared with stacking and unit type flexographic printing presses, flexographic heat shrinkable film is more suitable for CI type flexographic printing presses. This is because each color group shares an impression cylinder during the printing process, and the printing material and impression cylinder are tight. The tight fit, the change of tension is small, so that the stretching deformation of the material is small, and the registration accuracy is high.
2. Selection of ink
There are four main types of inks used for shrink film printing: solvent-based inks, water-based inks, cationic UV inks and free radical UV inks. In terms of application, in the field of shrink film label printing, solvent-based inks dominate, followed by water-based inks and free radical UV inks, while cationic UV inks tend to shrink due to their high price and troublesome printing. There are not many applications in the field of membranes. Solvent-based inks are mainly used in gravure and flexographic heat shrinkable films. Different films should use special inks and cannot be mixed. Ink companies generally provide three solvent ratios of fast-drying, medium-drying, and slow-drying inks corresponding to different materials. The printing plant can choose the appropriate solvent ratio according to the actual production conditions such as workshop temperature and printing speed. In addition, water-based inks and UV inks can also be used. However, no matter what type of ink is selected, it must be fully considered that the performance indicators of the ink must meet the requirements. For example, the shrinkage rate of the ink must match the shrinkage characteristics of the heat shrinkable film, otherwise the ink layer may split or even deink.
3. Control of drying temperature
When printing heat shrinkable film, how to control the drying temperature is very important. If the drying temperature is too high, the material will heat shrink; if the temperature is too low, the ink will not dry completely, resulting in final adhesion and dirt on the back. Both the gravure printing machine and the flexo printing machine are equipped with inter-color drying devices to ensure the complete drying of each color ink. At the same time, in order to prevent the material from deforming during the drying process, it is required to set up a cold air channel between the color sets to control the influence of residual heat. Today's printing presses use a freezing drum to quickly reduce the temperature of the material during the printing process. Because shrink film has common printability, such as strong chemical stability, low surface energy, smooth surface and no absorption, it has poor affinity with printing inks. Therefore, no matter what printing method is used, the film needs to undergo corona discharge treatment on the surface to increase its surface energy and roughness, and to improve the adhesion fastness of the ink on the surface of the material.


 English
English Español
Español русский
русский 简体中文
简体中文